백준 1330
두 수 비교하기

if 문 사용하기
if ~ else if ~ else
(if ~ else if ~ else if 하면 틀렸다고 함)
[나의 정답]
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int A,B;
A = in.nextInt();
B = in.nextInt();
if(A>B) {
System.out.println(">");
}else if(A<B) {
System.out.println("<");
}else {
System.out.println("==");
}
}
}
백준 9498
시험 성적

[처음에 틀린 답안]
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int score;
score= sc.nextInt();
if(score <= 100) {
System.out.println("A");
}else if(score < 90) {
System.out.println("B");
}else if(score < 80) {
System.out.println("C");
}else if(score < 70) {
System.out.println("D");
}else {
System.out.println("F");
}
sc.close();
}
}위처럼 100이하 A , 90이하 B ~ 했는데 틀렸다고 한다
아래 정답처럼 score >= 90 && score <= 100 해야 통과
[정답]
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int score;
score= sc.nextInt();
if(score >= 90 && score <= 100) {
System.out.println("A");
}else if(score >= 80 && score < 90) {
System.out.println("B");
}else if(score >= 70 && score < 80) {
System.out.println("C");
}else if(score >= 60 && score < 70) {
System.out.println("D");
}else {
System.out.println("F");
}
sc.close();
}
}
[다른 정답 2]
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int score;
score= sc.nextInt();
String grade;
if(score >= 90 && score <= 100) {
grade = "A";
}else if(score >= 80 && score < 90) {
grade = "B";
}else if(score >= 70 && score < 80) {
grade = "C";
}else if(score >= 60 && score < 70) {
grade = "D";
}else {
grade = "F";
}
System.out.println(grade);
sc.close();
}
}
[삼항연산자로 했을 때]
BufferedReader 를 써서 readLine() 을 통해 입력 받아 출력한다
BufferedReader 은 String 타입이라서 Integer.parseInt()를 써서 int로 형변환을 꼭 해줘야한다.
삼항연산자 란?

import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int score = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
System.out.println((score>=90)?"A": (score>=80)?"B": (score>=70)?"C": (score>=60)?"D": "F");
}
}
백준 2753
윤년

윤년은 연도가 4의 배수이면서, 100의 배수가 아닐 때 또는 400의 배수일 때이다.
4의 배수 and 100의 배수가 아닐때 or 400의 배수
and , or 잘 보고 풀기
[나의 정답]
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int year = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
if(year%4==0 && year%100!=0 || year%400==0) {
System.out.println("1");
}else{
System.out.println("0");
}
}
}
백준 14681
사분면 고르기
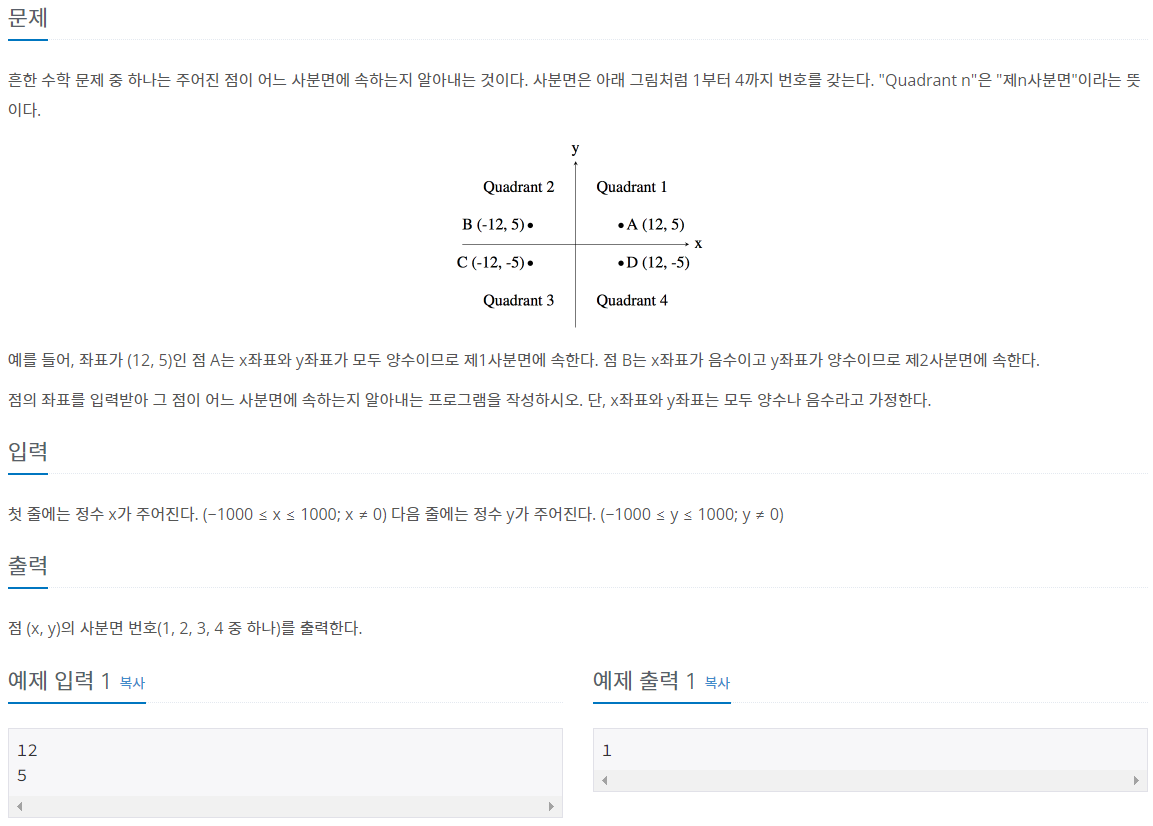
1사분면 (양,양)
2사분면 (음,양)
3사분면 (음,음)
4사분면 (양,음)
[ if ~ else if 사용한 정답]
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int X,Y;
X = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
Y = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
if(X > 0 && Y > 0) {
System.out.println("1");
}else if(X < 0 && Y > 0) {
System.out.println("2");
}else if(X < 0 && Y < 0) {
System.out.println("3");
}else {
System.out.println("4");
}
}
}
[ if 절을 사용한 정답]
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int X,Y;
X = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
Y = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
if(X > 0) {
if(Y > 0) {
System.out.println("1");
}else {
System.out.println("4");
}
}
if(X < 0) {
if(Y > 0) {
System.out.println("2");
}else {
System.out.println("3");
}
}
}
}
백준 2884
알람 시계

알아야할 것!
1. 분이 0~44분 사이라면 -45 할때 시간도 -1 이 된다.
2. 분이 45이상이면 분만 -45 하면된다.
3. 시(hour)가 0보다 작아질 경우 시(hour) 을 23으로 수정해준다.
▷자정 0시 45분(24시 45분) 이하일때 알람은 시간이 0 보다 작아질 경우니까 23시로 해준다
(제일 헷갈림)
1. 분이 0~44분 사이일때
10시 30분 알람을 맞춰놓으면 45분 전에 알람이 울린다.
10시 30분 - 45 ▶ 9시 45분
시간 계산법 : H - 1
분 계산법 : 60 - (45 - M)
2. 분이 45분 이상일때
분 계산법 : M - 45
[나의 정답]
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int H = sc.nextInt();
int M = sc.nextInt();
sc.close();
if(M >= 0 && M <= 44) {
H = H - 1;
M = 60 - (45 - M);
if(H < 0) {
H = 23;
}
System.out.println(H +" " + M);
}else {
M = M - 45;
if(H < 0) {
H = 23;
}
System.out.println(H +" " + M);
}
}
}
[BufferedReader]
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()," ");
int h = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if(m >= 0 && m <= 44) { // 분이 44분 이하일때
h--;
m = 60 - (45 - m);
if(h < 0) { //0시 45분 이하일때 23시로 해준다
h = 23;
}
System.out.println(h+" "+m);
}else { // 분이 45분 이상일때 분만 -45
System.out.println(h+" "+(m - 45));
}
}
}
백준 2525
오븐 시계

위의 알람시계 문제는 -45를 했다면 이번 문제는 오븐시간을 더하는 문제.
입력한 시간과 분에서 오븐사용 할 시간(분)을 더해 끝나는 시간을 출력해야한다.
오븐시간 1,000 분이하까지 더할 수 있는데 한시간만 생각하고 적었음.
if(m + oven > 60) {
h++;
오븐 시간이 몇시간이 될 수 있으니 시간을 모두 분으로 변환하고 연산 후 시간,분으로 바꾸기
풀이 방법
1. 오븐시간 60분 넘으면 / 60 몫 값을 시간에 더한다 , 분은 % 60 나머지 값을 더한다
2. 오븐시간 60분 아래면 (분 + 오븐시간) 더한다.
3. 그런데 (분 + 오븐시간) 더했을때 60분이 넘으면 시간을 +1 하고, 분은 -60
4. 시간이 24시 넘었을때 -24 해서 0시 1시 2시 .. 로 계산한다.
[나의 정답]
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int H = sc.nextInt();
int M = sc.nextInt();
int C = sc.nextInt();
sc.close();
// 0 ≤ H ≤ 23, 0 ≤ M ≤ 59, 0 ≤ C ≤ 1,000
if(C >= 60) {
H = H + C / 60;
M = M + C % 60;
}else {
M = M + C;
}
if(M >= 60) {
H++;
M = M - 60;
}
if(H >= 24) {
H = H - 24;
}
System.out.println(H + " " + M);
}
}
더 깔끔한 다른 풀이는
시간과 분을 모두 분으로 계산하고 다시 시간과 분으로 나누기
1. 먼저 시와 분을 모두 분으로 변환한다. 그리고 오븐시간까지 더하면 총 요리시간(분)이 나온다
int min = H * 60 + M;
min = min + C; // 오븐시간 더하기
2. 총 요리시간을 다시 시간과 분으로 계산한다.
시간은 % 60을 해서 나온 몫이고, 분은 /60 해서 나온 나머지
예를들어 min = 100분이 걸렸다. 시간은 %60했을때 몫인 1이고 분은 /60했을때 나머지인 40이다.
hour = min / 60;
minute = min % 60;
이때 24시 이상부터는 0시,1시..로 계산하기 위해 시간에서 %24를 해야한다.
hour = (min / 60) % 24;
[분으로 계산 후 다시 시와 분으로 나눈 풀이]
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int H = sc.nextInt();
int M = sc.nextInt();
int C = sc.nextInt();
sc.close();
int min = H * 60 + M; // 입력한 값을 모두 분으로 변환
min = min + C; // 오븐시간 더하기
int hour = (min / 60) % 24; // 24시 이상일때 0시,1시..로 되도록 %24 해서 나머지값으로
int minute = min % 60;
System.out.println(hour + " " + minute);
}
}
[BufferedReader]
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()," ");
int h = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int oven = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int min = 60 * h + m ; // 분으로 변환
min += oven;
h = (min / 60) % 24; // 24시 이상이면 0시,1시,2시 계산
m = min % 60;
System.out.println(h+" "+m);
}
}
백준 2480
주사위 세개

먼저 조건부에 a,b,c가 같은 경우를 썼다. 그다음 두쌍만 같은 경우. 마지막 모두 다른경우.
if(a==b && a==c) ~ else if(a==b || a==c) ~ else
아래의 코드가 왜 틀렸는지 의문...
a,b,c 공통값 ~ else if 는 두값만 공통값 ~ else의 조건식은? 정확하지 않아서인가
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
int c = sc.nextInt();
if(a==b && a==c) {
System.out.println(10000+a*1000);
}else if(a==b || a==c) {
System.out.println(1000+a*100);
}else {
if(a>b && a>c) {
System.out.println(a*100);
}else if(b>a && b>c) {
System.out.println(b*100);
}else {
System.out.println(c*100);
}
}
}
}
다시 수정한 풀이
▶ if(a==b && a==c) ~ else if(a!=b && b!=c && a!=c) ~ else if(a==b || a==c) ~ else
앞에서 else if(a==b || a==c) a가 공통값이고 다음 else는 b,c가 공통값
[정답]
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
int c = sc.nextInt();
if(a==b && a==c) { // a,b,c같을때
System.out.println(10000+a*1000);
}else if(a!=b && b!=c && a!=c) { // a,b,c 같지 않을때
if(a>b && a>c) { //a가 클때
System.out.println(a*100);
}else if(b>a && b>c) { //b가 클때
System.out.println(b*100);
}else { //c가 클때
System.out.println(c*100);
}
}else if(a==b || a==c) { //a가 b혹은 c와 같은 값일때
System.out.println(1000+a*100);
}else { //b와 c가 같은 값일때
System.out.println(1000+b*100);
}
}
}
[max를 이용한 다른풀이]
순서가 중요
먼저 if 조건식에 a,b,c 모두 같지 않을때 경우를 쓴다. ( 모두 같을때 조건식을 적으니 if else if 가 꼬였다..)
그다음 else 조건은 공통된 값이 하나라도 있는 경우이다.
else 안에는 모두 공통된 값 조건식과 두개만 공통된 값 조건식을 적는다
if (a != b && b != c && a != c) { // a,b,c 모두 같지 않을때
}
else { // a,b,c 공통된게 한 쌍이라도 있을때
if (a == b && a == c) { // a,b,c 모두 같을때
} else { // a,b,c 중 두 쌍만 같은 때
if (a == b || a == c) { // a가 공통값
} else { // b,c 같은값
}
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
int c = sc.nextInt();
if(a != b && b != c && a != c) { //a,b,c 같지 않을때
int max;
if(a > b) {
if(a > c) {
max = a;
}else {
max = c;
}
}else {//b가 더 클때
if(b > c) {
max = b;
}else {
max = c;
}
}
System.out.println(max*100);
}
else {
if(a==b && a==c) { // a,b,c같을때
System.out.println(10000 + a * 1000);
}else {
if(a == b || a == c) {
System.out.println(1000 + a * 100);
}
// b가 c랑 같은 경우
else {
System.out.println(1000 + b * 100);
}
}
}
}
}
[BufferedReader]
package CondingTest;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()," ");
int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int c = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if(a != b && a != c && b != c) { // 모두 다를때
int max;
if(a > b) { // a>b
if(a > c) { // a>(b,c)
max = a;
}else {
max = c; // c>(a,b)
}
}else { // b>a
if(c > b) { // c>b>a
max = c;
}else { // b>c>a
max = b;
}
}
System.out.println(max * 100);
}else { // 한 쌍이라도 같을 때
if(a == b && a ==c){ // 모두 같을때
System.out.println(10000 + a * 1000);
}else {
if(a == b || a ==c) { //a가 b,c와 같을 경우
System.out.println(1000 + a * 100);
}else { // b,c가 같을 경우
System.out.println(1000 + b * 100);
}
}
}
}
}'공부' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준] 3단계 | 반복문 8~12 (0) | 2023.02.17 |
|---|---|
| [백준] 3단계 | 반복문 1~7 (0) | 2023.02.14 |
| [백준] 1단계 | 입출력과 사칙연산 10~14 (0) | 2023.01.26 |
| 입력방법 BufferedReader (0) | 2023.01.20 |
| [백준] 1단계 | 입출력과 사칙연산 1~9 (0) | 2023.01.20 |